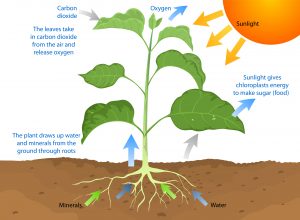
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants transform the sun’s energy into food energy.
©Shutterstock: Mapichai
All living things need energy in order to live, grow, and reproduce. Green plants get their energy from the sun. In a process called photosynthesis, sunlight activates the green chlorophyll in leaves to convert carbon dioxide from air and water from soil into starches and sugars (called carbohydrates), which are the plant’s food.
Plants need air and water to live. Carbon dioxide from air and water are the main ingredients for photosynthesis. Water is also an important part of the plant’s structure and helps to transport nutrients from the soil to the plant’s roots.

Trees and other plants need water to live. ©Shutterstock: Herjua
Most plants depend on soil for support and to provide nutrients. Some plants—like aquatic plants that grow in water—do not need soil, but they get nutrients from the substance in which they grow.
Plants also need space to grow. If they do not have enough space and if they must compete with neighboring plants for nutrients, light, and water, plants may find it difficult to survive and grow.
In this activity, your class will design an experiment to test whether these basic requirements are, in fact, necessary.
A scientific experiment must have a control group and an experimental group. The control group should be kept under normal conditions, that is, given normal amounts of space, water, light, etc. The experimental group is kept under normal conditions in all aspects except for the one variable being tested. After the experiment is completed, you can compare the groups. If there are any important differences between them, you can conclude that the differences are due to the one factor that was different.
Discussion Questions
-
- What do plants need to live and grow?
- Where do plants get food energy?
- What is the difference between a control group and experimental group in a scientific experiment?